Audiology Services & Fees
Comprehensive Hearing Services
HEARING SAVERS provides a complete range of audiological services at very competitive prices
| Audiology Service | Our Price |
|---|---|
| Hearing Test - Pension Card Holder | FREE |
| Hearing Test - Veteran (DVA) Card Holder | FREE |
| Hearing Test - NDIS | FREE (paid by NDIS) |
| Hearing Test - WorkCover | FREE |
| Hearing Test - Health Care Card Holder | $62.00 $100
BULK BILLED* |
| Hearing Test - Private Adult | $82.00 $120
BULK BILLED* |
| Hearing Test - Aviation, Police, Pre-Employment | $62.00 $75 |
| Ear Wax Removal | $95.00 |
| Hearing Aid Adjustment & Service | $62.00 |
| Custom Ear Plugs (each) | Varies |
| Hearing Aid Repairs | Varies |
| Hearing Aid Batteries | from $2.85 per packet |
| Hearing Aids | SAVE $3,000+ |
Contact us on 1800 00 HEAR (1800 00 4327)
* From 1 March 2023, hearing tests at HEARING SAVERS Bentleigh, Caulfield, Malvern and Essendon hearing clinics are BULK BILLED under Medicare when you have a referral from your doctor.
Hearing Evaluation
On your first visit to HEARING SAVERS, we will start by asking you questions about your medical and hearing history. This is called the case history. Next, the audiologist will look into your ears using a light, called an otoscope, and check for anything in the ear canal that might affect the test results or require referral to your doctor. Finally, the audiologist will conduct a test or series of tests to assess:
- Whether there is a hearing loss
- The cause of the hearing loss (to the extent possible)
- The degree and configuration (one or both ears?) of hearing loss
- The best treatment options
The Audiogram
The audiogram is a graph showing the results of the pure-tone hearing tests. It illustrates the type, degree, and configuration of hearing loss.
The frequency or pitch of the sound is referred to in Hertz (Hz). The intensity or loudness of the sound is measured in decibels (dB). The responses are recorded on a chart called an audiogram that shows intensity levels for each frequency tested.
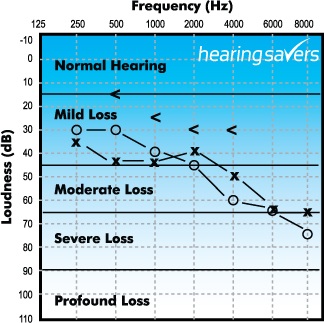
Each vertical line from left to right represents a pitch, or frequency, in Hertz (Hz). The graph starts with the lowest pitches on the left side and moves to the very highest pitches (frequencies) tested on the right side. The range of frequencies tested are 125 Hz, 250 Hz, 500 Hz, 1000 Hz, 2000 Hz, 3000Hz, 4000 Hz, and 8000 Hz.
- Examples of sounds in everyday life that would be considered “low-frequency” are a bass drum, tuba, and vowel sounds such as “oo” in “who.”
- Examples of sounds in everyday life that would be considered “high-frequency” are a bird chirping, a triangle being played, and the consonant sound “s” as in “sun.”
Each horizontal line on the audiogram from top to bottom represents loudness or intensity in units of decibels (dB). Lines at the top of the chart (-10 dB and 0 dB) represent soft sounds. Lines at the bottom of the chart represent very loud sounds.
- Examples of sounds in everyday life that would be considered soft are a clock ticking, a voice whispering, and leaves rustling.
- Examples of sounds in everyday life that would be considered loud are a lawnmower, a car horn, and a rock concert.
On the audiogram, the pattern of hearing loss (configuration) and degree are recorded. For example, your hearing might be normal in the low pitches while you have hearing loss in high pitches. In this case, you might hear speech, but it would sound muffled and unclear. If you have hearing loss at all pitches, you might have difficulty hearing any speech.
The audiologist uses a red O to indicate the right ear and a blue X to record the left ear. The farther down the audiogram the Xs and Os appear, the worse the hearing.

























